| advertisement: compare things at compare-stuff.com! |
Since the prediction method is based on simple Euclidean geometry and
relies upon protein domains of different structural classes occupying
different, but overlapping, regions in composition space, the prediction
accuracy for a particular query should correlate inversely with the
proximity of the query composition vector to an intersection of these fuzzy
regions. A simple reliability measure, ![]() , based on this assumption has
been calculated as follows:
, based on this assumption has
been calculated as follows:
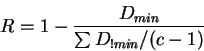
where ![]() is the Euclidean distance between the query
sequence composition and the closest (i.e. predicted) class centroid,
is the Euclidean distance between the query
sequence composition and the closest (i.e. predicted) class centroid,
![]() is the sum of the non-minimal distances between query
sequence composition and class centroids, and
is the sum of the non-minimal distances between query
sequence composition and class centroids, and ![]() is the total number of
class centroids (3 in this case). For query sequences approximately
equidistant to each centroid,
is the total number of
class centroids (3 in this case). For query sequences approximately
equidistant to each centroid,
![]() . Larger values for
. Larger values for ![]() occur when the query sequence is closer to one centroid than the others, on
average.
occur when the query sequence is closer to one centroid than the others, on
average.
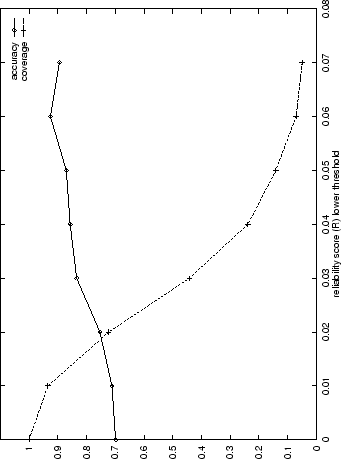 |
In Figure 3.2 the prediction accuracy, ![]() , and the
prediction coverage (i.e. the fraction of sequences for which a prediction
is made) are shown for a range of thresholds of
, and the
prediction coverage (i.e. the fraction of sequences for which a prediction
is made) are shown for a range of thresholds of ![]() (prediction details as
for Result 20 in Table 3.1). Clearly as predictions are
filtered using higher thresholds for
(prediction details as
for Result 20 in Table 3.1). Clearly as predictions are
filtered using higher thresholds for ![]() the fraction of correct predictions
increases. The coverage decreases quite rapidly, however.
the fraction of correct predictions
increases. The coverage decreases quite rapidly, however. ![]() is
93% for predictions which satisfy
is
93% for predictions which satisfy ![]() , but this high level of
reliability is only expected in 7% of predictions (see coverage in
Figure 3.2). The top 44% of predictions (
, but this high level of
reliability is only expected in 7% of predictions (see coverage in
Figure 3.2). The top 44% of predictions (![]() ) are
83% accurate. In Section 3.4 prediction accuracies are
given for four quartiles based on ranking the predictions by
) are
83% accurate. In Section 3.4 prediction accuracies are
given for four quartiles based on ranking the predictions by ![]() .
.