



Next: Antigen contacts - CDR
Up: Results
Previous: Results
Contents
Contact Analysis
Solvent accessibilities and antigen contacts were computed for all residues
in the 26 antibody-antigen complex structures
(Table 2.1). Figures 2.1 & 2.2
summarize this information for each of the six CDRs. The bar graphs show
how many antibody structures have solvent accessible or antigen contacting
residues at each sequence position. The line graphs compare contacts made
by different antigen types (see Figure legends for details).
Table 2.1:
Antibody crystal structures (complexed with antigen - total 26) - PDB July 1995
|
PDB code |
name |
antigen |
antigen type |
interface area (Å ) )
![[*]](/icons/latex2html/icons/footnote.png) |
antigen size class![[*]](/icons/latex2html/icons/footnote.png) |
resolution/R-factor |
topography![[*]](/icons/latex2html/icons/footnote.png) |
|
|
2mcp |
McPC603 |
phosphatidyl choline |
hapten |
32.63 |
small |
3.1Å /18.5% |
moderately concave |
|
|
1fig |
1F7 |
TSA![[*]](/icons/latex2html/icons/footnote.png) for chorismate mutase (catalytic) for chorismate mutase (catalytic) |
hapten |
54.97 |
small |
3.0Å /22.0% |
moderately concave |
|
|
1dbb |
DB3 |
progesterone |
hapten |
71.61 |
small |
2.7Å /21.0% |
concave |
|
|
1eap |
17E8 |
phosphonate TSA (catalytic) |
hapten |
76.46 |
small |
2.5Å /18.6% |
concave |
|
|
4fab |
4-4-20 |
fluorescein |
hapten |
81.89 |
small |
2.7Å /21.5% |
concave |
|
|
1baf |
AN02 |
DNP-spin-label |
hapten |
82.40 |
small |
2.9Å /19.5% |
planar |
|
|
2cgr |
2cgr |
cyanophenyl diphenylmethyl guanidineacetic acid |
hapten |
87.73 |
small |
2.2Å /21.4% |
concave |
|
|
1igj |
26-10 |
digoxin |
hapten |
91.19 |
small |
2.5Å /17.6% |
concave |
|
|
1ind |
CHA255 |
indium(3+)-eotube |
hapten |
96.81 |
small |
2.2Å /18.8% |
moderately concave |
|
|
1ibg |
40-50 |
ouabain |
hapten |
101.47 |
small |
2.7Å /20.9% |
concave |
|
|
1mfb |
SE155-4 |
heptasaccharide |
carbohydrate |
118.88 |
medium |
2.1Å /16.0% |
concave |
|
|
1acy |
59.1 |
HIV-1 GP120 peptide |
peptide |
128.04 |
medium |
3.0Å /21.0% |
ridged |
|
|
1fpt |
C3 |
poliovirus type 1 peptide |
peptide |
128.18 |
medium |
3.0Å /23.0% |
ridged |
|
|
1ggi |
50.1 |
16aa peptide HIV-1 GP120 |
peptide |
135.47 |
medium |
2.8Å /18.8% |
moderately concave |
|
|
1him |
17 9 9 |
8&9aa peptides from flu. HA |
peptide |
137.23 |
medium |
2.9Å /20.0% |
ridged |
|
|
1cbv |
BV04-01 |
ssDNA (Auto-antibody) |
dna |
139.19 |
medium |
2.7Å /19.1% |
ridged |
|
|
2igf |
B13I2 |
myohemerythrin residues 69-87 |
peptide |
146.65 |
medium |
2.8Å /22.0% |
ridged |
|
|
1tet |
TE33 |
cholera toxin peptide 3 |
peptide |
150.19 |
medium |
2.3Å /14.8% |
ridged |
|
|
1ikf |
1ikf |
cyclosporin A |
cyc-peptide |
168.00 |
large |
2.5Å /16.4% |
ridged |
|
|
1jhl |
D11.15 |
pheasant egg lysozyme |
protein |
174.42 |
large |
2.4Å /21.4% |
planar |
|
|
1jel |
JE142 |
histidine containing protein |
protein |
191.50 |
large |
2.8Å /19.3% |
concave |
|
|
1vfb |
D1.3 |
hen egg lysozyme |
protein |
193.05 |
large |
1.8Å /18.5% |
planar |
|
|
1mlc |
D44.1 |
hen egg lysozyme |
protein |
198.26 |
large |
2.1Å /18.4% |
planar |
|
|
3hfm |
HyHEL-10 |
hen egg lysozyme |
protein |
223.56 |
large |
3.0Å /24.6% |
moderately concave |
|
|
2hfl |
HyHEL-5 |
hen egg lysozyme |
protein |
248.47 |
large |
2.54Å /24.5% |
moderately concave |
|
|
1ncd |
NC41 |
neuraminidase (N9 Whale) |
protein |
266.22 |
large |
2.9Å /15.7% |
planar |
|
Table 2.2:
Antibody crystal structures (Fab/Fv only - total 19) - PDB July 1995
|
PDB code |
name |
antigen |
antigen type |
resolution/R-factor |
topography![[*]](/icons/latex2html/icons/footnote.png) |
|
|
1fai |
R19.9 |
anti-arsonate (Xtal 2) |
hapten |
2.7Å /18.9% |
concave |
|
|
1lmk |
L5MK16 |
anti-phosphatidylinositol scFv |
hapten |
2.6Å /20.0% |
ridged |
|
|
2gfb |
CNJ206 |
catalytic (esterase) |
hapten |
3.0Å /21.3% |
concave |
|
|
6fab |
36-71 |
anti-phenylarsonate |
hapten |
1.9Å /20.9% |
moderately concave |
|
|
1gig |
HC19 |
influenza virus hemagglutinin |
peptide |
2.3Å /19.5% |
concave |
|
|
1bbj |
B72.3 |
tumour marker (sialyl-Tn) (humanised) |
carbohydrate |
3.1Å /? |
concave |
|
|
2fbj |
J539 |
anti-galactan |
carbohydrate |
1.95Å /19.4% |
planar |
|
|
1mam |
YST9.1 |
lipopolysaccharide A antigen of
Brucella abortus |
carbohydrate |
2.5Å /21.5% |
concave |
|
|
1bbd |
8F5 |
anti-HRV2 |
protein |
2.8Å /19.0% |
ridged |
|
|
1dfb |
3D6 |
anti-HIV-GP41 |
protein |
2.7Å /17.7% |
concave |
|
|
1fgv |
H52 |
humanised anti-CD-18 (Some of H3 missing) |
protein |
1.9Å /18.0% |
planar |
|
|
1for |
Fab17-IA |
anti-human rhinovirus |
protein |
2.75Å /17.4% |
concave |
|
|
1fvc |
Hu-4D5 |
ERBB2 receptor extracellular portion (hum.) |
protein |
2.2Å /18.3% |
moderately concave |
|
|
1rmf |
R6.5 |
anti-ICAM-1 |
protein |
2.8Å /18.8% |
concave |
|
|
1igc |
MOPC21 |
bound to Streptococcus Protein G Domain III |
unknown |
2.6Å /16.8% |
ridged |
|
|
1igm |
HuIgM |
human IgM Fv |
unknown |
2.3Å /20.1% |
planar |
|
|
2fb4 |
Kol |
myeloma Fab |
unknown |
1.9Å /18.9% |
planar |
|
|
7fab |
New |
unsure |
unknown |
2.0Å /16.9% |
moderately concave |
|
|
8fab |
Hil |
human myeloma |
unknown |
1.8Å /17.3% |
moderately concave |
|
(a) CDR-L1
 |
(b) CDR-L2

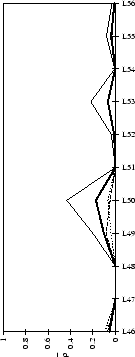 |
(c) CDR-L3

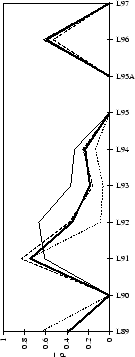 |
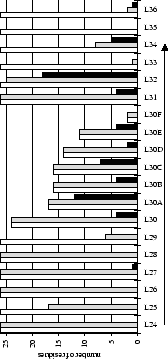
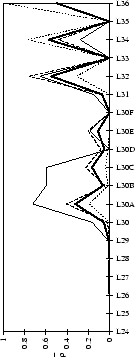
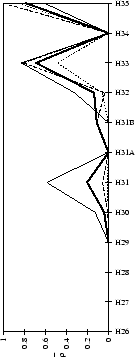
Figure 2.1:
Contact analysis for light chain
antigen contacts. Unfilled bars: number of antibodies with residues at
each sequence position. Grey bars: number of antibodies with accessible
residues at sequence position. Black bars: number of antibodies making
antigen contacts at each position (see Methods). Line graphs:
 mean fractional burial by antigen type (see Methods).
Thick solid lines: all antigens. Fine dashed lines: small antigens (see
Table 2.1 column 6). Medium dashed lines:
medium sized antigens. Thin solid lines: large antigens. Arrows mark the
standard CDR definitions (see Table 2.3). Where
these differ the dashed arrows denote the Kabat sequence variability
definition; the solid arrows denote the Chothia loop definition. Arrows
point towards the centre of combining site (see
Figure 2.3).
mean fractional burial by antigen type (see Methods).
Thick solid lines: all antigens. Fine dashed lines: small antigens (see
Table 2.1 column 6). Medium dashed lines:
medium sized antigens. Thin solid lines: large antigens. Arrows mark the
standard CDR definitions (see Table 2.3). Where
these differ the dashed arrows denote the Kabat sequence variability
definition; the solid arrows denote the Chothia loop definition. Arrows
point towards the centre of combining site (see
Figure 2.3).
(a) CDR-H1
 |
(b) CDR-H2

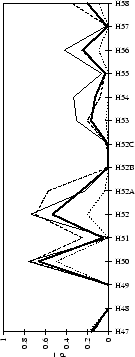 |
(c) CDR-H3
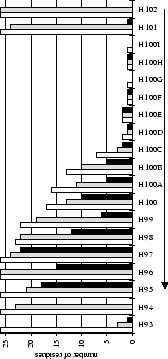
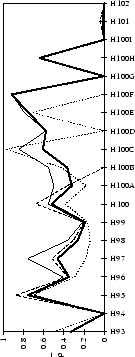 |
Figure 2.2:
Contact analysis for heavy chain antigen
contacts. See legend to Figure 2.1. Note that in
CDR-H2 the sequence variability definition extends to H65.
The two main CDR definitions (Table 2.3) are shown in
Figures 2.1 & 2.2 with arrows pointing towards the
centre of the combining site (Figure 2.3). All residue
numbering follows the scheme of Chothia et
al.chothia:d13,chothia:canon.
Table 2.3:
CDR definitions - all residue
numbering follows the scheme of Chothia et al.chothia:canon.
| CDR |
Kabat 1 |
Chothia 2 |
Contact
range3 |
| L1 |
L24 - L34 |
L24 - L34 |
L30 - L36 |
| L2 |
L50 - L56 |
L50 - L56 |
L46 - L55 |
| L3 |
L89 - L97 |
L89 - L97 |
L89 - L96 |
| H1 |
H31 - H35 |
H26 - H32 |
H30 - H35 |
| H2 |
H50 - H65 |
H52 - H56 |
H47 - H58 |
| H3 |
H95 - H102 |
H95 - H102 |
H93 - H101 |
|
- 1 sequence variability[Wu & Kabat, 1970]
- 2 loop definition[Chothia et al.,
1986,Chothia & Lesk, 1987]
- 3 start and
end residues must satisfy
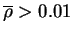 and make at least one
antigen contact (see Methods) in the set of complexes (see Table 2.1) and make at least one
antigen contact (see Methods) in the set of complexes (see Table 2.1)
|
Figure 2.3:
CDR arrangement. Contact CDR definitions (see
Table 2.3) are shown in strong colours, residues
defined by other CDR definitions are shown in grey.
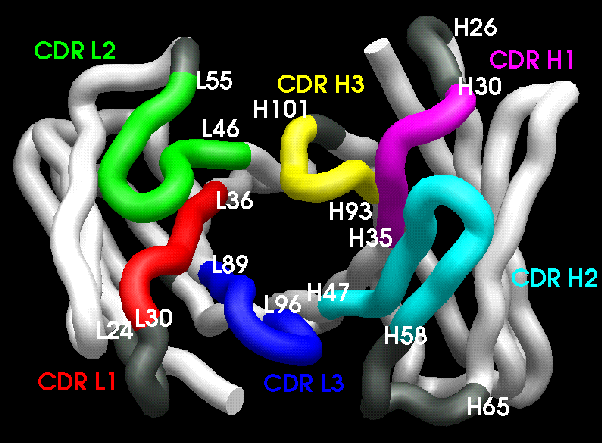 |
Only two antigen contacts are made by residues
not shown in Figures 2.1 & 2.2. These
were L67 in antibody HyHEL-10 (3hfm, anti-lysozyme[Padlan et al.,
1989]) and
H64 in antibody NC41 (1ncd, anti-neuraminidase[Tulip et al., 1992]). Tables
of the numeric data are available on the
internet![[*]](/icons/latex2html/icons/footnote.png) .
.
Subsections




Next: Antigen contacts - CDR
Up: Results
Previous: Results
Contents
Copyright Bob MacCallum
- DISCLAIMER: this was written in 1997 and may contain out-of-date information.

![]() .
.