| advertisement: compare things at compare-stuff.com! |
The non-contacting residues within the CDRs coincide with residues identified by Chothia et al.chothia:HVRegions as important in defining canonical backbone conformations. Since, by definition, the side-chains of canonical key residues pack internally, they make few antigen contacts.
The variation in backbone conformations for the different canonicals is
summarised in Figure 2.4. This highlights the broad
conservation of different forms of CDR-L2, CDR-L3 and CDR-H2 and higher
variability of CDR-L1, CDR-H1 and CDR-H3.
In order to analyse the contacts made by the different CDR
conformations, the mean fraction burial by antigen (
![]() , see
Section 2.2.2) is calculated for each CDR representative and is
plotted in three dimensions in a `composite combining site'
(Figure 2.4). This shows that, in general, only the
central part of the combining site makes antigen contacts. The contact
epicentre is displaced towards the heavy chain CDRs.
, see
Section 2.2.2) is calculated for each CDR representative and is
plotted in three dimensions in a `composite combining site'
(Figure 2.4). This shows that, in general, only the
central part of the combining site makes antigen contacts. The contact
epicentre is displaced towards the heavy chain CDRs.
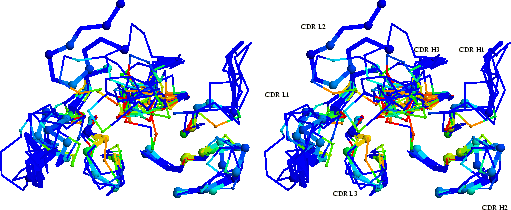 |
Antigen contacts made by specific backbone conformations can be compared in CDR-L1 and CDR-H2, where there are sufficient numbers of different examples (6 or more). These two CDRs are shown in detail in Figure 2.5. Where CDR residues in two different canonical conformations are in the same position and orientation, the average contacts made are qualitatively similar. The insertion in CDR-L1 alters the sidechain orientations of residues L30 and L31 (Figures 2.5(a) and (b)) such that in the longer class 4 loop these never make contacts (in the shorter class 2 loop they do make contacts).
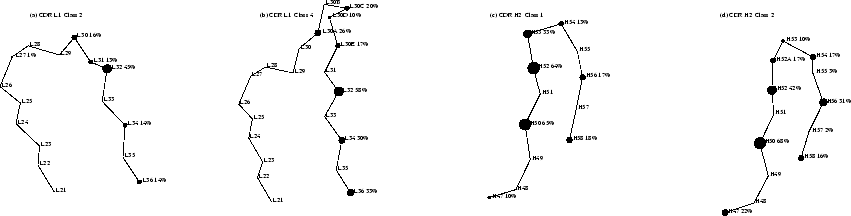 |